Art of the State

Creative Genius
The reclusive Mel Chin creates deeply engaging artwork at an international scale
By Liza Roberts
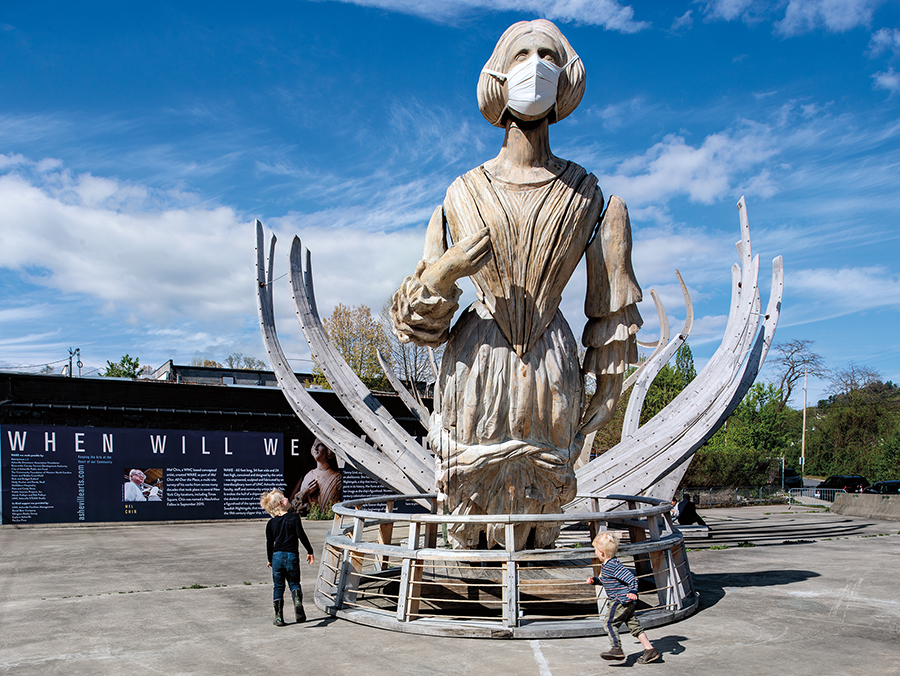


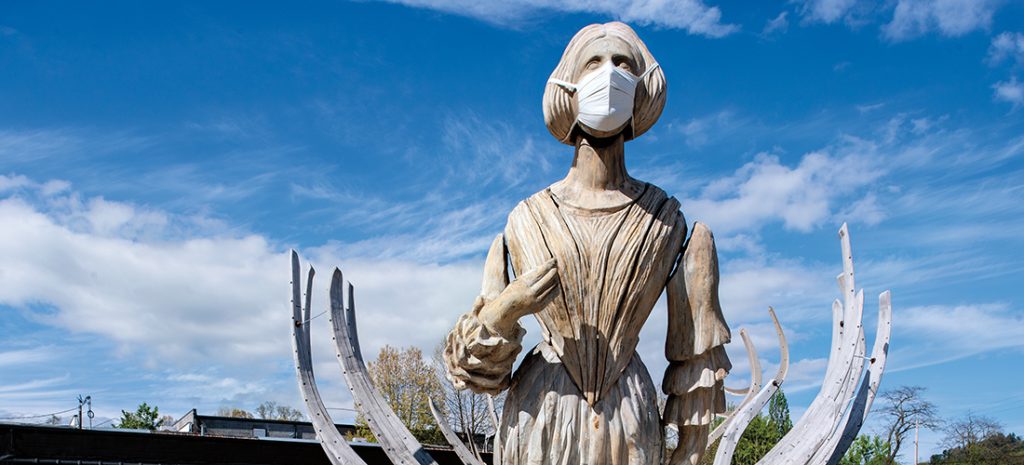
Wake, 2018
The only visual artist in North Carolina ever to win a MacArthur Genius award, Mel Chin manages to hide in plain sight in his home state, where only the most art-informed even know he’s here.
Tucked into Higgins, N.C., a distant corner of Yancey County near the Tennessee border, this world-renowned artist has space and time for his creativity to expand and his engagement with the wider world to ignite. His massive public sculpture, augmented-reality, subversive video, collage and interactive installations address issues as wide-ranging as climate change, political division, the environment, community health and the Black Lives Matter movement.
Chin says his conceptual work is a tool for civic engagement and a way to raise awareness of social issues. Through art, he believes questions can be asked and possibilities raised in uniquely effective ways. “I have always described the practice of art as providing an option, as opposed to an answer,” he says, sitting back in the shade of a porch at his stone house. Ivy and overgrown shrubs blur its edges as the Cane River rushes nearby.
He was here in 2019 when the MacArthur people called to tell him of his remarkable award, including its no-strings-attached check for $650,000. Chin “is redefining the parameters of contemporary art and challenging assumptions about the forms it can take, the issues it can address, and the settings it can inhabit,” the Foundation said in announcing its decision.
“When people ask about what inspires you,” Chin says, “I no longer speak in terms of inspiration, but of being compelled. Because how could you not?” The issues that compel him are not necessarily new, he points out, but they’re in the news, which provides new opportunities.
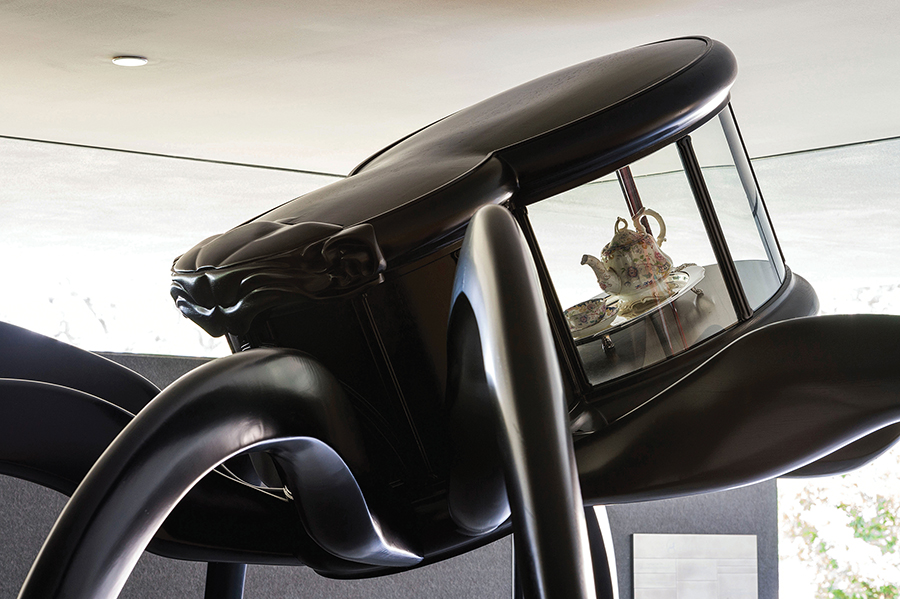
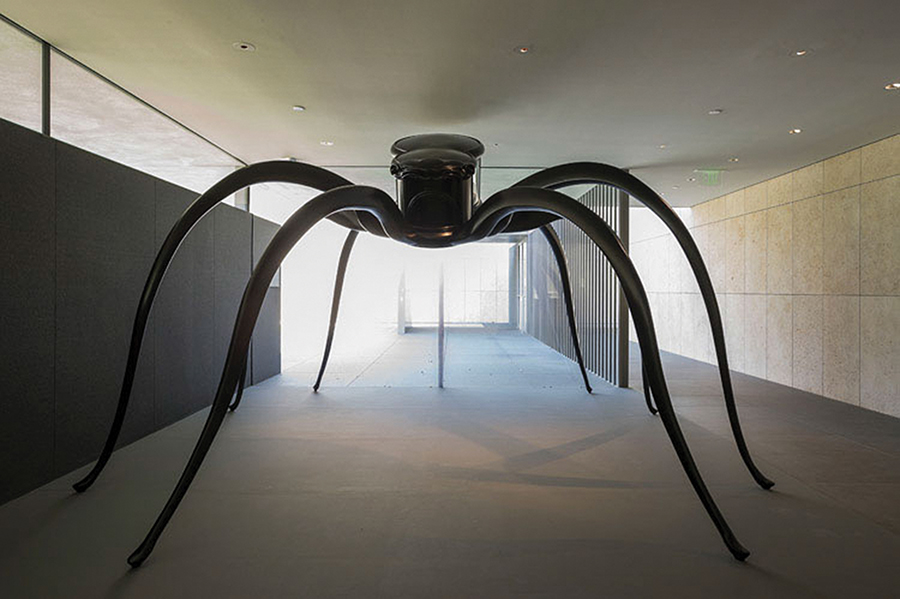


Cabinet of Craving, 2012
Remote as he is, much of Chin’s work is done in collaboration with others, near and far. His 60-foot-tall animatronic sculpture Wake, which resembles both a shipwreck and a whale skeleton, was created with University of North Carolina Asheville students and was installed in Asheville’s South Slope after forming the focal point of a larger installation in Manhattan’s Times Square. There it was accompanied by Unmoored, a mixed-reality mobile app he designed with Microsoft that depicted the square as if it were 26 feet under water, submerged by rising sea levels. It was one of several installations in a New York City-wide survey of Chin’s works in 2018.
The creative expression of scientific information and the use of technology to inspire empathy is a Chin hallmark. One ongoing project uses plants to remediate toxic metals from the soil; a Mint Museum installation used oceanographic data to create “cinematic portraits” of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans; and a viral, community-based work circulates hand-drawn hundred dollar bills to draw attention to lead contamination in soil, water and housing. “You could say that I’m involved with the process of bridging science and community,” he says.
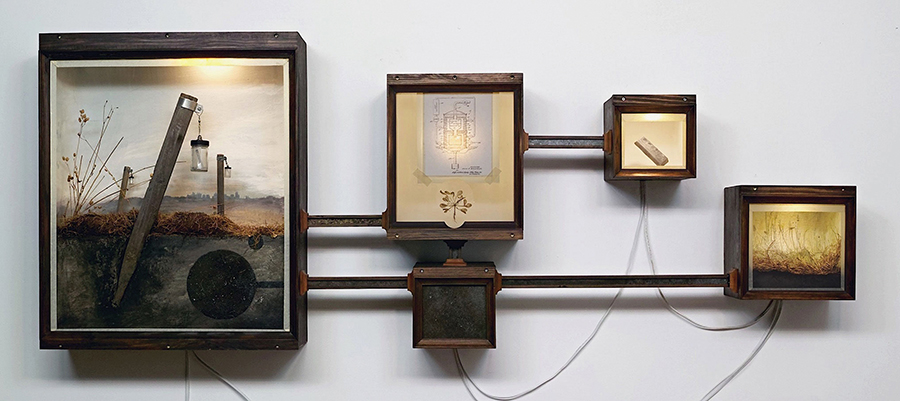

Revival Field (Diorama), 2019, mixed media, 40 x 66 x 8 in
Community in the traditional sense seems far removed from his remote corner of the world, but Chin’s dogged social conscience, regular travel, wide network and the connected reality of 21st-century life keep him plugged in. He’s turned the stately 1931 stone mansion at the center of his compound into a rambling archive and workshop for his many artistic pursuits. The mansion was originally built as a library and community center for the creation and distribution of local crafts. It became part of a regional study on poverty and was visited in 1934 by Eleanor Roosevelt; it also served as a school and was used as a birthing hospital. The place had fallen into disuse and disrepair when Chin acquired it in the late 1990s as an inexpensive place to store his work. A few years later, he left New York, where he had lived for many years, and moved here himself — not into the mansion, but into the relatively modest house a few feet away, one originally built for the hospital’s chief doctor.
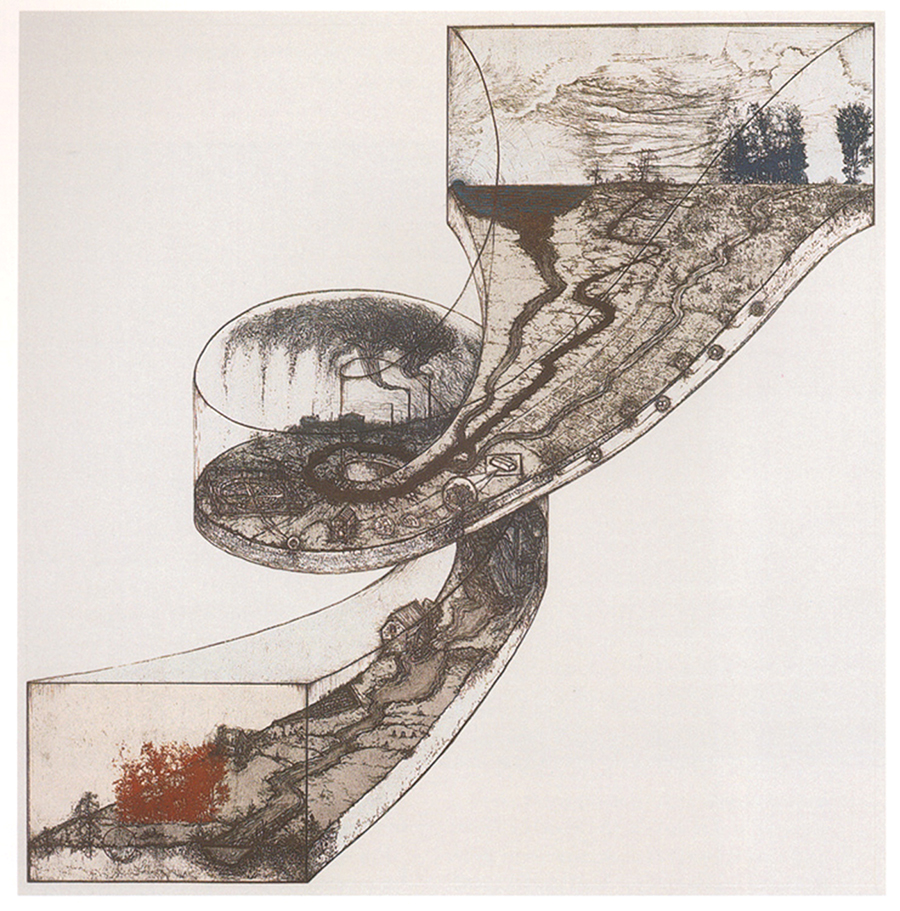
Etching Revival Ramp, 1996
Chin says he was drawn to this part of the country not just for space and the chance to live deeply within the natural world, but also by the region’s history of racial injustice and his own lifelong commitment to fighting it. The American-born child of Chinese immigrant parents, Chin grew up in Houston in the 1950s, worked at his parents’ grocery store in the city’s predominantly African-American Fifth Ward, and became aware of and thoughtful about issues surrounding race from an early age.
“To be engaged in the world,” he says, “it’s OK to be in places where the engagement is very real and uncomfortable.” Lately, that engagement transcends geography. “It’s an important time,” Chin says. “We’re at this bridge. It’s about consolidating a commitment to actually begin again, listen more and reorient actions, and respond.” The role of an artist, he says, is to “excavate” the questions such issues provoke, provide a starting point and draw collective attention. Still, Chin points out that from his perspective, the “job description of artist” is constantly evolving: “People think it’s kind of funny when I say that I’m still trying to be one, to be an artist. But I mean it, actually.” OH
This is an excerpt from Art of the State: Celebrating the Art of North Carolina, published by UNC Press.
